In the blob compressor, the acceptable tolerance is the amount of variation allowed between equivalent blobs in the clustering process.
Describes a color aberration due to heterogeneous pixel spacing. For example, if it occurs in the sampling, due to harmonics between the sampling and event frequencies, it is known as a Johnson alias. On a monitor, it is more likely due to inductive ringing in the monitor cable.
An Internet server operator that allows end users to run one or more programs over the Internet on an associated server.
A special characteristic of text character (such as Bold or Italics).
A computer process that runs without user assistance.
A mismatch between two semiconductors (usually transistors) where the same bias results in different amounts of conductivity.
A mathematical compound that can be used to approximate a curve with a mathematical equation. In its most common form, it has a beginning, an end, and two control points, where the control points are used to bend the shape of the curve.
A description of a two color image. For example an image that has black and white but no shades of gray.
The smallest data element inside a computer. It has two states which are denoted as a 1 and a 0.
[First Definition] A method of storing an image by using a single bit to represent one of two colors (usually black and white).
[Second Definition] A non-proprietary file format that (in most cases) saves each color of each pixel as one byte. The file extension is usually *.BMP.
A group of adjacent pixels that are all exactly the same color. A blob is sometimes used synonymously with region, but a region is often used as a group of adjacent pixels that are combined together. A region contains the implication that the pixels may not all be exactly the same color.
For example, a region might be used to refer to the entire area of a light gray can sitting on a black background (the background would not be part of the region). The light gray can might have slightly darker gray decorations, but the whole would still be in the same region.
A proprietary raster compressor that is built into Pac-n-Zoom®. It is a geometrical compressor with hierarchical ordering.
A place where one color stops and another color starts. A border implies an abrupt change whereas a transition doesn't.
These are also known as charge coupled semiconductors. They are semiconductors that are specially fabricated to detect light. They are the sensors used in cameras and scanners to change light into electricity. On this site, the issues presented by CCDs are considered to be the same as those from light diodes and CMOS sensors.
Optical systems have an exact focus at a specific wavelength of light. Since light usually has more than one wavelength, distortions occur because the light does not match the exact wavelength the optical system is focused at. Therefore chromatic aberations are essentially aberations resulting from different colors (or wavelengths) of light.
An electronic noise that mixes the clock signal into another signal. This usually occurs from inductive and capacitive coupling between traces on a circuit board or integrated circuit. The affect is compounded because the rising edge of the clock can cause many transistors to switch simultaneously.
In the blob compressor, a cluster is a constellation of patterns that repeated within the acceptable tolerance.
In printing and other real processes, color bleeding is considered a problem. It is when two adjacent colors get mixed together. In the virtual world, color bleeding is often a desired effect.
A noise that occurs because the color shade is half way between two discrete values and the color presented vacillates between those values. As an analogy, a digital speedometer has flutter when the car is going 54.5 miles per hour, and the speedometer vacillates between 54 and 55.
A major part of the Pac-n-Zoom program. The color segmenter segments a color while image enhancing the quality of the picture by performing image restoration.
[First Definition] A file whose data records are delimited by commas. These are used primarily by spread sheets and databases.
[Second Definition] A non- proprietary file format supported by Pac-n-Zoom and has an extension of *.CDL. It is easily parsed into databases for the purposes of debug.
A text based interface where the user enters commands at a prompt (such as a DOS prompt).
The initial user command is interactive, but the interface can be manipulated into a batch processing mode.
A term used to describe an image whose color is constantly changing. The implication is that each pixel is a slightly different color than the preceding pixel.
A term used to describe the visible edges of a blob. Contour lines are often used in negative sense to describe a photograph that doesn't have enough colors.
The amount of color change divided by the number of pixels. Therefore, large and fast color changes have a high contrast.
A device that integrates data, instructions, libraries, or other elements over a series of iterations.
Thermodynamic noise in a charged coupled device.
A Pac-n-Zoom filter that eliminates repeating single pixel vacillations on the edges of segmented blobs. It is incorporated into the segmenter. The data resolver is incorporated inside the blob compressor.
A group of data inside a frame as shown in the following example.
The part of the Pac-n-Zoom technology that converts raster into primitive vector.
A non-von-Neumann computer that has two parts. The first part is called the data tagger and it passes judgments on incoming data. These judgments become instructions and are passed to a convolver. The convolver is usually a conventional (von Neumann) computer or a state machine that accepts separate data and instructions.
Optics will focus at some specific distance. The depth of field will indicate how well a specific part of a picture will focus by how far it varies from the focal point.
The discreet cosine transform converts spatial information to "frequency" or spectral information, with the X and Y axes representing frequencies of the signal in different dimensions. This
allows for "lossy" compression of image data by determining which information can be thrown away without compromising the image.
The DCT is used in many compression and transmission codecs, such as JPEG,
MPEG and others. The pixels when transformed are arranged from the most significant pixel to the least significant pixel. The DCT functions themselves are lossless. Pixel loss occurs when the least significant
pixels are quantitized to 0 (from nyx.net).
A wavelet-based (but uses other technologies as well) technology originally be Bell Labs (AT&T). In 2000, DjVu was acquired by Lizard Tech.
An industry that deals with moving paper files to the computer.
A subset of the document handling industry that deals with converting the document from a paper to an electronic representation.
Segmentation that finds the edges of blobs to build a border around the blob.
The process of pulling information from a picture. The information could be any thing. Some typical extractions are recognition, location, color, area, and perimeter.
Any parameter of an image. Some typical features are edges, colors, areas, and locations.
The style of text character (such as Courier or Times Roman).
A set of data that pertains to a configuration, data, or command. Frames are found in text files. The syntax or example of a frame can be found here.
An electronic device (usually a computer board) that stores at least one video frame.
A compression algorithm that reduces geometrical shapes into a more efficient representation (usually tags). Geometrical compressors are not currently popular because they require a segmented image to provide competitive compression.
A proprietary statistical compressor with its name (GIF) used as the file extension.
The glider is the part of the Pac-n-Zoom system that promotes the primitive vector into the final output. The final output might be raster or another form of vector.
An interactive user interface usually dominated by a mouse, track-ball, or some other pointing device. In the predominant interaction, the user points at a screen icon and clicks a button to select the process the icon represents.
An abbreviation for high definition television. It is the high definition television signal mandated in the United States. It is 1,080 lines and has 1920 pixels in a line.
When memory is dynamically allocated by the programmer (usually with a variation of malloc() and free()), the allocated memory is from the computer memory system known as the heap. The heap is allocated at run time.
A graph that plots the most predominant colors against a spectrum of colors.
An abbreviation for hypertext markup language. It is the publishing language of the world wide web. In other words, it is the standard format for an Internet page.
A statistical compression method that converts characters into variable length bit strings. Most-frequently occurring characters are converted to shortest bit strings; least frequent, the longest. Compression takes two passes. The first pass analyzes a block of data and creates a tree model based on its contents. The second pass compresses the data via the model. Decompression decodes the variable length strings via the tree. (from computing-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com)
The process of rebuilding a picture that was distorted by a known process.
Video that is created by interlacing (interweaving) to consecutive pictures to create a single picture.
In interlaced video, the first field is painted into every other line of the video display screen. The second field is then painted into the lines left blank.
A non-proprietary raster file format that is popular on the Amiga Computer. The file name extension is *.IFF.
An electronic noise with a thermodynamic origin. The voltage of Johnson noise is white noise with a voltage squared noise spectral density.
A standards committee that published a file format used for compression. The most popular version of it uses a discrete cosine transform to discard (hopefully) less significant colors.
A common file name extension for JPEG files is *.JPG.
Kilobytes or 1,000 bytes.
Abbreviation for local area network. It refers to the technology used to connect computers together. It assumes the computers are located within a few hundred feet of each other. For example, the computers in an office would be connected together with LAN technology.
A wavelet based file format developed by LuraTech.
LuraDocument is a registered trademark of LuraTech.
A single instruction in a higher level language that results in a series of instructions in a lower level language.
It is different from a subroutine, because a macro implies the sub-instructions are in a different language.
[First Definition] A language designed to write macro instructions (usually for another language).
[Second Definition] In the Pac-n-Zoom® system the macro language is a set of internal instructions for a specific application that allows a master script (such as Python, Pearl, Rexx, or others) to operate several applications as a single solution.
The Pac-n-Zoom program would be one application. Other applications must be modified to accept the script commands before they can use this system.
Megabytes or 1,000,000 bytes.
The process of putting data samples together to construct a model for rendering by another program. For example, a number of raster photographs could be used together to build a 3D model for an animation database.
An anacronym that stands for: Motion Picture Experts Group. It is usually associated with compressing audio and video files.
Unwanted aberrations and distortion in an electronic signal. Some common types of electronic noise are clock coupling, color flutter, dark current, Johnson noise, among many others.
Almost all computers use von Neumann architecture which uses separate instructions and data. A non-von-Neumann computer is any computer where the data is the instructions.
An abbreviation for National Television Standards Committee. It is the conventional television signal broadcasted in the United States and some other countries.
Also known as "Nyquist Theorem" and "Shannon Sampling Theorem". It was written by Nyquist in 1928 and mathematically proven by Shannon in 1949. As it applies to us, an artifact needs to be sampled at least twice or the picture will be distorted. Therefore, orphan pixels have been proven to be unreliable because the final constellation of pixels (needed for extraction) is impossible.
An abbreviation for optical character recognition. OCR is a computer reading and recognizing text in a document.
In physics, wave front optics are optics that deal with waves of light. On this site, wave front optics refer to those optics that try to focus a picture (as opposed to optics that manipulate light without attempting to reach a focus - for example the concentration or the dispersion of light). The variation from the optimal focus causes distortions which Pac-n-Zoom Pre.View partially corrects.
A pixel with no adjacent neighbor of the same color.
A data file format that is specific to the Pac-n-Zoom program. Its extension is *.PNZ.
A mechanism that allows memory contents to be moved or shared between progams. The process is called piping.
The size of a text character (such as 10 or 12)
A single picture element such as a dot on a page or a point of light on computer screen.
An open sourced statistical compressor (pronounced ping) and idd after its file extension.
A series of lines that are connected end to end (in mathematics it called a polygonal chain). They can be used to define the border of blob.
A color used to build other colors. In pigments (i.e., printing), four primary colors are usually used. They consist of magenta (purplish red), cyan (greenish blue), yellow, and black,
where black is used more for economy and contrast than as a building block. In light (i.e., computer monitors and television), red, green, and blue are usually used.
Primary colors are more of
an artistical approximation than a scientific building block.
The vector data outputted from the data tagger. The primitive vector can be reduced to raster or promoted to another vector type.
In Pac-n-Zoom the process controller is a piece of software that takes the I/O from the master script and distributes it among the client processes. The process contoller allows Pac-n-Zoom or other enabled software to be controlled by the master script. In other words, the process controller allows Pac-n-Zoom to be easily integrated into an existing software design without recompilation.
This memory is fixed in size at the compile time. It is usually a static or a global. Since they have an exact size, they are placed within a section of the final linked executable file.
Data represented by a series of dots or pixels. To the computer, the dots are all disconnected, therefore the ability to extract information from the data is usually limited to the Fourier and associated transforms.
A computer simulation of light used to design optics and to enhance vector data.
A group of pixels that need to be taken together to extract a feature. As an example, consider a black letter "A" on a white background. The feature is the letter "A". The extraction we require is recognition. The "A" is considered to be black, but it could be 20 different shades of black. A region would include all 20 shades of black.
A computer program that allows a remote user to operate a computer over a computer network.
Vector data that can be accurately processed by a mathematical routine.
The process of creating more dots or pixels in raster data. The number of artifacts remains the same, but the grain of the picture is finer.
[First Definition] Pac-n-Zoom comes with a system for using multiple programs together (provided that their interface is extended).
Instructions and data can be stored in this simple system. A segment is used to store either instructions or data inside of a rame.
[Second Definition] The process of performing segmentation.
The process of grouping pixels that are nearly the same color into regions and blobs.
In an image, the maximum speed of pixel to pixel change. For example, a black to white border might take several pixels to transition. The slew rate would be the most change between any two pixels of the transition.
This is memory that is allocated for a process. It is generally used when a function is called. The calling function's state is stored on the stack until the function is returned.
An entity that provides a computing solution. The most common type of a solution provider is a value added reseller (VAR), but consultants, integrators, distributors, and other IT professionals (or amateurs) might also be solution provides.
A compression algorithm that uses probabilistic analysis. One of the more common statistical compressors uses a binary tree and a tagging system.
When image color changes have a high degree of contrast, it usually takes several image pixels for the change to occur. For example a steady state color (plateau) might change over
several pixels (slope) before another plateau is reached. The steepest slope is the pixel that has the most pixel to pixel change. If more than one pixel has the same change, the pixel that is
furtherest away from the plateaus (or most central to the slope) is the steepest slope. If two pixels tie in centrality, the west pixel is the steepest slope.
The steepest slopes are the position
of the actual border before transition distortion clouded the image while it was being captured.
The process of putting data samples together into an aggregate data set. For example, several photographs might be stitched together to make a larger photograph or to construct a panoramic view.
The process of comparing one shape to another on a pixel by pixel basis. The number of pixels that match between the hapes determine whether the shapes match.
A computer program that is specifically designed to edit text.
Segmentation that uses absolute color to determine the blob a pixel resides in. For example, if black text were on white paper, any pixel darker than gray might be considered black (the foreground), and any pixel lighter than gray might be considered white (the background).
A compression system know as the tagged information file format (TIF or TIFF) used mostly in scanning and FAXing. A *.TIF can have one of several different compression systems. For example, the bi-tonal *.TIF G4 and G3 or TIFF G4 and TIFF G3 are the standards in the document handling and FAX industries respectively.
A compression algorithm that uses a mathematical transform. The most common transform is the discrete cosine transform which is closely related to the Fourier Transform.
A change in colors. A place where one color changes to another.
| transition distortion: | 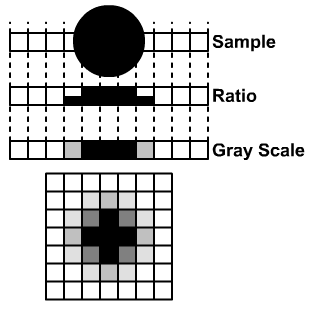
Unwanted artifacts introduced into an image along the edge of a blob usually by sampling errors as graphically demonstrated here. | |
|---|
Data represented in the form of mathematical equations.
The process of changing data, that is represented by a series of dots, into mathematical equations.
An abbreviation for Video Home System. VHS video tape has quality comparable to NTSC video.
A term used to describe a part (usually one half) of a video image. In NTSC (the conventional American television signal), two video fields are interlaced together to compose one video image (where a video image is usually referred to as a video frame).
A term used to describe one video image. In NTSC (the conventional American television signal), two video fields are interlaced together to compose one video frame.
A program that attempts to eliminate computer viruses from the computer system.
A set of mathematics that is normally used as a geometrical image compressor.